I brought three big red sword tails today but as soon as I put them in my 300L my albino ruby shark started going mad and he's constantly chasing them. He normally does it to other fish but only when I put food in. I tried catching the swordtails to move them to my my smaller tank but I can't for the life of me catch them. Is it just because they're new? Will he get used to them and eventually lay off?
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
How To Stop Bullying?
- Thread starter Samj11
- Start date
At my school, they have us attend seminars and ask our students to sign 'Anti-Bullying' pledges.
Ruby sharks are highly territorial, especially when new fish are added to their established territory - which is why they are often the last fish added. I would also suggest that the swordtails appear too similar to the ruby and so the aggression is focused on them. That's my understanding, though I've never kept the ruby sharks.
Ruby sharks are highly territorial, especially when new fish are added to their established territory - which is why they are often the last fish added. I would also suggest that the swordtails appear too similar to the ruby and so the aggression is focused on them. That's my understanding, though I've never kept the ruby sharks.
Tongue_Flicker
Fish Herder
What i usually do is take out the bully fish first then the remaining tankmates. Rearrange the decors, add more hides, add more plants then reintroduce the peaceful/neutral fishes first. Let them establish themselves for about a day then introduce the bully fish the next day. Kinda time consuming but hey works for me lol
eaglesaquarium said:Nice catch Akasha! I can't believe I didn't mention that. Too busy trying to be funny I guess. (Shame on me!)
hahaha, no worries. We can't remember everything all of the time! We're only human
He has laid off a bit and luckily there are four swordtails so it's not just one getting chased every time. I tried changing some decor around and to begin with it worked but he's back to being a bully again now lol. Moving him to my small tank isn't really an option as there are very small fish in there that he could easily harm or try to eat. It's frustrating as he's leaving the clown loaches, the gourami (most of whom are bigger than him) and the danios alone but constantly going for the swordtails whenever he sees them. Will he do this every time I get new fish? If so, I'm thinking I might have no choice but to get rid of him. I like peaceful tanks lol.
in my experience once a fish is a bully it will remain a bully. Try and see if you can find other ways to deflect the bullying - obviously I can't see your tank so I've no idea if you have plants etc but if you've got a bully it helps to provide area's of sanctuary for the other fish and the best way to do that is to plant heavily.
I often look in my tank and think ... where have all my fish gone ... but then I look closer and they're resting in the plants or hiding or just taking a break ... especially if there some breeding going on and it's a bit hectic
I often look in my tank and think ... where have all my fish gone ... but then I look closer and they're resting in the plants or hiding or just taking a break ... especially if there some breeding going on and it's a bit hectic
As I mentioned, there's two factors at work here...
1 - these fish (ruby sharks) are markedly territorial. So, this fish likely has set-up its territory and will work to defend it.
2 - these fish are highly intolerant of 'conspecific/congeneric' (fish of the same specie or genus) fish or fish which appear too similar in body type, and will harass them as they would their own specie.
So, in conclusion: one of two (or a combination) options are at work. 1 - the new fish aren't a part of his territory, and the hierarchy has not been established. 2 - the shark is reacting to fish that it considers to be a threat to it, and is acting accordingly.
It could be that the shark would not attack new fish of the same species you already have, or even completely different species that it doesn't consider similar to itself. It could be that the swords are too similar in appearance for this specific individual to feel that they are not a threat. Each shark is an individual and they all react differently. So, its a case by case thing.
If a major redesign of the tank doesn't provide for a settling in, then the only options I see are: 1 - remove the swords. They are the targets, and none of the others. 2 - remove the shark. He's the one causing the disruption to peace in the tank.
FYI:
 /seriouslyfish.com/species/Epalzeorhynchos-frenatum/
/seriouslyfish.com/species/Epalzeorhynchos-frenatum/
1 - these fish (ruby sharks) are markedly territorial. So, this fish likely has set-up its territory and will work to defend it.
2 - these fish are highly intolerant of 'conspecific/congeneric' (fish of the same specie or genus) fish or fish which appear too similar in body type, and will harass them as they would their own specie.
So, in conclusion: one of two (or a combination) options are at work. 1 - the new fish aren't a part of his territory, and the hierarchy has not been established. 2 - the shark is reacting to fish that it considers to be a threat to it, and is acting accordingly.
It could be that the shark would not attack new fish of the same species you already have, or even completely different species that it doesn't consider similar to itself. It could be that the swords are too similar in appearance for this specific individual to feel that they are not a threat. Each shark is an individual and they all react differently. So, its a case by case thing.
If a major redesign of the tank doesn't provide for a settling in, then the only options I see are: 1 - remove the swords. They are the targets, and none of the others. 2 - remove the shark. He's the one causing the disruption to peace in the tank.
FYI:
httpBehaviour and Compatibility:
A slightly better choice for the community tank than E. bicolor but tankmates must still be chosen with care.
While small specimens tend to hide away much of the time they become increasingly territorial as they grow and can display particularly high levels of aggression towards similar-looking species.
Some individuals may be more belligerent than others and there exist reports of apparent alliances with other species such as Chromobotia macracanthus. We’re unsure if these behavioural differences are indicative of gender but at any rate loaches from the genera Chromobotia, Botia, Syncrossus and Yasuhikotakia do seem to be left in peace by Epalzeorhynchos species whereas congenerics and members of Crossocheilus, Garra and Gyrinocheilus, for example, tend to be attacked constantly. Please note that in terms of the loaches not all may be housed together and proper research is essential.
Other bottom-dwelling fishes including cichlids and most catfish are best avoided as they may too be picked on. For the upper levels choose robust, active, schooling cyprinids. Ideally the Epalzeorhynchos should be the final addition to the tank in order to avoid it claiming ownership of the entire space.
This species probably lives a solitary lifestyle and in nature would probably have only come into contact with others of its own kind infrequently and during the spawning season. These instincts heighten as the fish get older and we therefore recommend it be kept singly in the majority of cases. In a very large tank with lots of cover a cohabitation attempt might be possible but each individual is likely to require a territory with a diameter of at least a metre.
 /seriouslyfish.com/species/Epalzeorhynchos-frenatum/
/seriouslyfish.com/species/Epalzeorhynchos-frenatum/JD has hit the nail directly on the head.
I have written elsewhere about the significant damage a "bully" fish does. Physical interaction we can see, but there is much more we cannot see. The chemical signals (pheromones and allomones) these fish are releasing are picked up and "read" by other fish, and they can be highly stressful too.
Fish hiding in the plants or behind something is a sign of real trouble, and should never be ignored. In time we learn to recognize when this is or isn't a problem, temporary spawning or permanent fear. But no fish should be forced into hiding.
Byron.
I have written elsewhere about the significant damage a "bully" fish does. Physical interaction we can see, but there is much more we cannot see. The chemical signals (pheromones and allomones) these fish are releasing are picked up and "read" by other fish, and they can be highly stressful too.
Fish hiding in the plants or behind something is a sign of real trouble, and should never be ignored. In time we learn to recognize when this is or isn't a problem, temporary spawning or permanent fear. But no fish should be forced into hiding.
Byron.
The chasing has died down and I've ordered a lot of big fake plants to fill up the tank more so they'll be able to avoid each other easier.
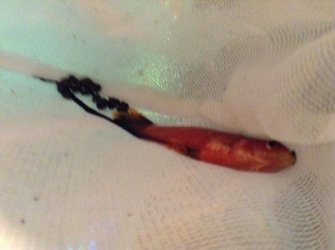
However, one of the swordtails appears to have something wrong with his mouth. After a Google search I assumed it was cotton mouth disease so I ordered Malafix which will be arriving tomorrow. Just wanted a second opinion so there are photos below. Could it be something else?


However, one of the swordtails appears to have something wrong with his mouth. After a Google search I assumed it was cotton mouth disease so I ordered Malafix which will be arriving tomorrow. Just wanted a second opinion so there are photos below. Could it be something else?


Now I know this is probably going to get a lot of flak...
When I first got my 36 gallon tank, my first two fish were male swordtails. One was bigger and dominant, and always abused the smaller one. Out of curiosity and n00bishness, I started using a net to separate the two fish any time the dominant male charged in, sometimes even isolating him for a few minutes using my net. Other times when the alpha male would try to creep up on the poor little fish, I would use my fingers and move them about (to make it look like there were fish on the other side). The big fish totally forgot what he was doing for a brief moment and I quickly tapped the glass in front of his face, sending him swimming away. I did this every time I saw the male attack. After less than 2 weeks of doing this they mostly stopped and a couple months after started "schooling," or as close to schooling as you can get with two fish.
When I first got my 36 gallon tank, my first two fish were male swordtails. One was bigger and dominant, and always abused the smaller one. Out of curiosity and n00bishness, I started using a net to separate the two fish any time the dominant male charged in, sometimes even isolating him for a few minutes using my net. Other times when the alpha male would try to creep up on the poor little fish, I would use my fingers and move them about (to make it look like there were fish on the other side). The big fish totally forgot what he was doing for a brief moment and I quickly tapped the glass in front of his face, sending him swimming away. I did this every time I saw the male attack. After less than 2 weeks of doing this they mostly stopped and a couple months after started "schooling," or as close to schooling as you can get with two fish.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 281